
1.首先路由方面要设计好了
app目录下子路urls.pyfrom collections import UserList
from django.urls import path, include
from APP.views import *
urlpatterns = [
# 首页
# path('list/', APP.views.index)
path('index/', index, name='index'),
path('userList/', userList, name='userList')
]
2.然后是渲染函数view视图对应两个
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
pass
return render(request, 'userIndex.html')
def userList(request):
return render(request, 'userList.html')
3.接下来就是django中html特有的一些语法书写
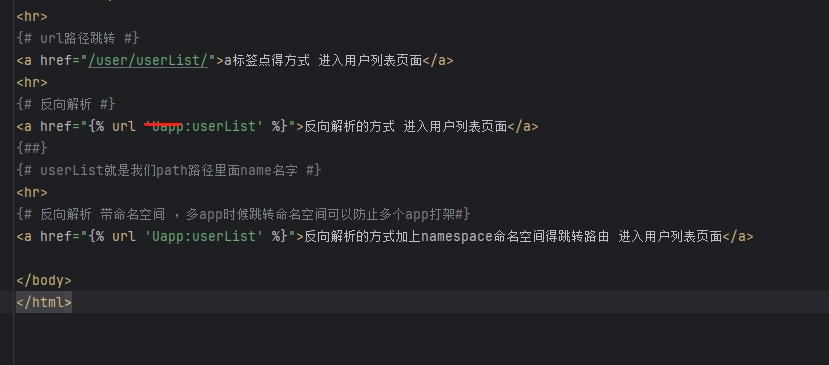
第三种跳转方案 具体要看跟路由有没有配置路由命名空间 就一个app就可以省略
# 2. 使用子路由 namespace 命名空间
urlpatterns += [
# path('user/', include('APP.urls', 'APP'), namespace='user')
path('user/', include(('APP.urls', 'APP'), namespace='Uapp')),
]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>用户首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>用户首页</h1>
<hr>
{# url路径跳转 #}
<a href="/user/userList/">a标签点得方式 进入用户列表页面</a>
<hr>
{# 反向解析 #}
<a href="{% url 'Uapp:userList' %}">反向解析的方式 进入用户列表页面</a>
{##}
{# userList就是我们path路径里面name名字 #}
<hr>
{# 反向解析 带命名空间 ,多app时候跳转命名空间可以防止多个app打架#}
<a href="{% url 'Uapp:userList' %}">反向解析的方式加上namespace命名空间得跳转路由 进入用户列表页面</a>
</body>
</html>
|